 Vocabulary:
Vocabulary:
carbohydrate: an organic compound made of sugar molecules
monosaccharide: simple sugars that contain just one sugar unit
disaccharide: sugar with two monosaccharides
polysaccharide: long polymer chain made up of simple sugar monomers
starch: a polysaccharide found in plant cells that consists entirely of glucose monomers
glycogen: excess sugar in a form of a polysaccharide
cellulose: polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers that reinforce plant-cell walls
This section discusses about the definition of carbohydrates and how carbohydrates provide energy. In a dehydration reaction, cells create two monomers, becoming disaccharides ( the main type of disaccharide is sucrose ). Long polymer chains of simple sugar monomers are polysaccharides, such as starch, a polysaccharide found in plant cells consisting entirely of glucose monomers. When plants break down s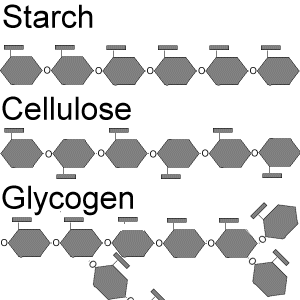 tarch molecules, the glucose becomes available to use. Animals and humans store sugar in a type of polysaccharide called glycogen. Just like starch, glycogen is also a chain of many glucose monomers. When the glycogen is needed in animals, the body breaks down the energy from glycogen granules releasing glucose. Cellulose are polysaccharides that protect cells and stiffens plants. Cellulose is also made of glucose monomers. Most animals and people cannot digest cellulose because they do not contain the molecule necessary to break the bonds of the glucose monomers in glucose. All carbohydrates are hydrophilic. Starch comes from plants and glycogen comes from humans and animals.
tarch molecules, the glucose becomes available to use. Animals and humans store sugar in a type of polysaccharide called glycogen. Just like starch, glycogen is also a chain of many glucose monomers. When the glycogen is needed in animals, the body breaks down the energy from glycogen granules releasing glucose. Cellulose are polysaccharides that protect cells and stiffens plants. Cellulose is also made of glucose monomers. Most animals and people cannot digest cellulose because they do not contain the molecule necessary to break the bonds of the glucose monomers in glucose. All carbohydrates are hydrophilic. Starch comes from plants and glycogen comes from humans and animals.
Concept Checks
1. Explain the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide. Give an example of each. Monosaccharides contain one sugar unit ( simple sugars ) and a disaccharide contains two sugar units ( double sugars ). An example of a monosaccharide is fructose and an example of a disaccharide is sucrose.
2. Compare and contrast starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all polysaccharides. Glycogen is found in animals and humans and a glycogen polymer is more highly branched than starch polymer. Cellulose is found in plants, just like starch, but they work as building materials. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all made of glucose monomers.
3. How do animals store excess glucose molecules? Animals store excess glucose molecules in glycogen. When the body needs energy, it breaks down glycogen granules, releasin glucose.

No comments:
Post a Comment